The performance requirements for plastic mold materials are not as high as those for cold-work and hot-work mold materials. However, plastic molds typically have complex structures, low surface roughness requirements, and high precision demands. Therefore, plastic mold materials must ensure excellent processing performance.
1. Performance Requirements for Plastic Mold Materials
The main performance requirements for plastic mold materials are as follows:
(1) Hardness and Wear Resistance
The surface of the plastic mold cavity should have sufficient wear resistance. Typically, the hardness of plastic mold materials ranges from 38 to 55 HRC. For molds with simple shapes and high polishing requirements, a higher hardness is preferred; conversely, for molds with less complex shapes, a lower hardness may be suitable.

(2) Strength and Toughness
The strength and toughness of the plastic mold materials must ensure that the mold does not deform or crack under the forces of mold opening, melt pressure, and clamping force.
(3) Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance refers to the ability of the plastic mold material to withstand the corrosive gases (such as HCl or HF) released when plastics containing chlorine or fluorine elements are heated to their molten state.

(4) Heat Resistance and Dimensional Stability
Plastic mold materials should have a stable microstructure and low thermal expansion coefficient to ensure that the mold does not oxidize or deform during long-term operation at temperatures ranging from 160°C to 250°C.
(5) Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity refers to the material's ability to efficiently dissipate heat, enabling the plastic part to cool and solidify quickly in the mold cavity.
2. Process Performance Requirements for Plastic Mold Materials
The process performance requirements mainly include machinability, mirror polishing ability, texture processing ability, heat treatment processability, weldability, and electro-machinability.
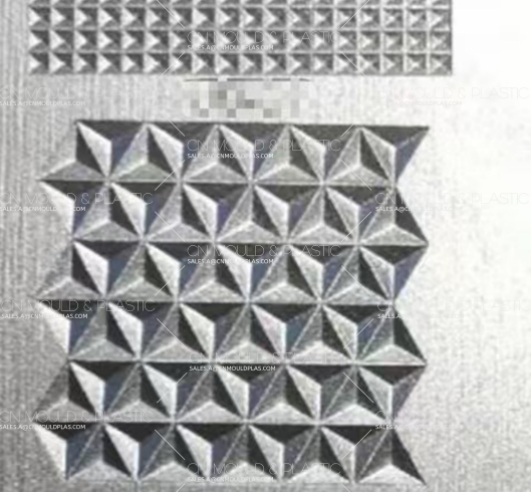
Plastic mold cavities are typically complex, and their surface quality requirements are high. Therefore, mold materials should possess excellent cutting and grinding performance. As the demand for transparency in plastic products increases, the need for high-quality mirror polishing on the mold surface also rises. Many plastic products also require decorative patterns, which means the mold material must have good texturing capabilities.
Plastic mold materials should also have sufficient hardenability and through-hardening capacity. The tendency for distortion and cracking during heat treatment should be minimal, and heat treatment quality should be stable.
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) and wire-cutting are common electro-machining methods used in plastic mold processing to create complex mold cavities. However, the hardened layer, grooves, and cracking generated during electro-machining can negatively affect the mold. Therefore, plastic mold materials must exhibit good electro-machining properties.

