Key Performance Indicators (KPI) are important for businesses because they help them monitor and evaluate performance in real time. By setting the right KPI, companies can better understand their internal operations, identify problems and make adjustments in a timely manner, thus ensuring that they maintain an edge in a competitive market. Here are a few effective KPI:
1) Reportable Health and Safety Incidents - Measures the number of actual accidents or threatening health and safety incidents that have occurred over a period of time.
2) Reportable Environmental Incidents - Measures the number of environmental incidents that have occurred over a period of time.
3) Number of Non-Compliance Events/Year - A measure of the number of times a factory exceeds normal regulatory compliance rules in a year. For specific non-compliance times, causes and solutions, complete documentation is required.
1) Percentage Planned vs. Emergency Maintenance Work Orders -- This ratio indicator is an indicator of how often planned maintenance occurs, not more disruptive/unplanned maintenance.
2) Downtime in Proportion to Operating Time--The ratio of downtime to operating time is a direct indicator of the availability of production assets.
l Increase flexibility and innovation
1) Rate of New Product Introduction -- represents how quickly a new product can be introduced to market and usually includes a combination of design, development and manufacturing acceleration times.
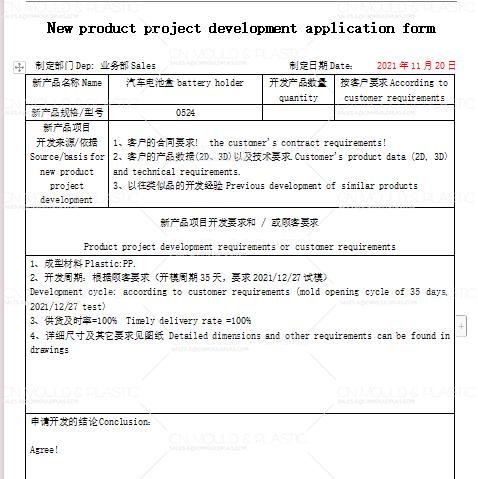
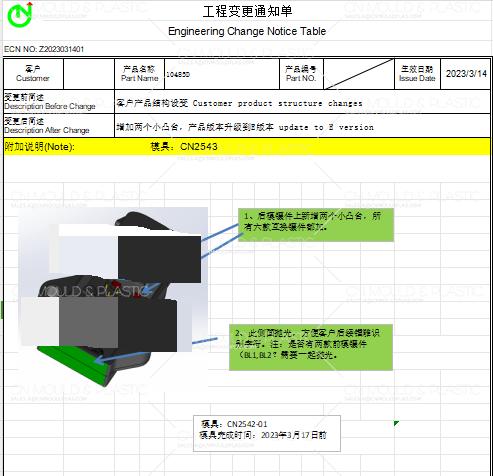
2) Engineering Change Order Cycle Time -- Measure the rate of design changes or modifications to existing products. This can be achieved through documentation processes and mass production.
1) Total Manufacturing Cost per Unit Excluding Materials
2) Manufacturing Cost as a Percentage of Revenue - The ratio of total manufacturing costs to the total revenue of a manufacturing plant or business unit.
3) Net Operating Profit - Measure the financial profitability of all investors/shareholders/creditors of a manufacturing plant or business unit, before or after tax.
4) Productivity in Revenue per Employee - This is a measure of the revenue generated by a plant, business unit, or company divided by the number of employees.
5) Average Unit Contribution Margin - This metric is calculated by dividing the profit margin generated by a manufacturing plant or business unit by a given unit or volume of production.
6) Return on Assets/Return on Net Assets - A measure of financial performance calculated by dividing the net income of a manufacturing plant or business unit by the value of deployed fixed assets and working capital.
7) Energy Cost per Unit - A measure of the cost of energy (electricity, steam, oil, gas, etc.) required to produce a specific unit or volume of production.
8) EBITDA - This acronym stands for earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization. EBITDA is often used as a top indicator of a business's current operating profitability.
9) Customer Fill Rate/ On-time delivery/ Perfect Order Percentage -- This indicator is the percentage of times that a customer receives all the products ordered, meets the correct specifications and is delivered on the expected Time.