1) For injection molding machines with a clamping force of 1000 kN or below, the distance between the venting should be 50mm; for machines with a clamping force above 1000 kN, the distance should be 75mm.
2) At the intersections of the corners on both sides of the plastic part, the venting should be set at a 45° angle.
1) The strength and toughness of the plastic mold materials must ensure that the mold does not deform or crack under the forces of mold opening, melt pressure, and clamping force.
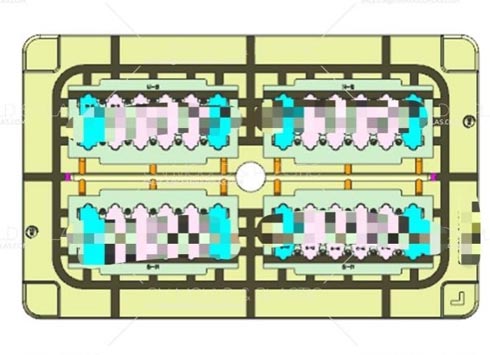
2) The width of the venting should be 3–5mm.
3) The length of the venting should be 3.175–19mm (0.125–0.75 inches, determined by the amount of sealing).
4) The venting channel should open to the atmosphere, with a typical depth of 0.50–0.80mm.
5) The cross-section displays the depth, width, and distance from the mold cavity for trapezoidal and circular venting. The designer must use their judgment to select the recommended standard dimensions. The cross-sectional area of the venting channel must be at least greater than the sum of the cross-sectional areas of all the venting holes leading to the venting.
6) Continuous venting holes. The dimensions of the venting holes should fall within the following range:
① Depth: 0.01–0.02n, determined by the amount of injected plastic.
② Length: 1.0mm, 1.5mm, or 2mm, determined by the cavity size.
③ Width (venting holes): minimum of 2mm, with a preference for 5–6mm (if possible, uninterrupted venting should be used). If the product does not allow such wide venting holes, narrower (1–2mm) holes are acceptable.
If sufficient space is available, it is better to use larger venting channels, as larger tools can be used, and the venting channels are easier to process.